Patient Reported Outcomes and The Growth of Digital Health Technology
Clinical Trials
An update to our blog about how digital health technology is optimizing the clinical research industry.
Introduction to Digital Health Technologies
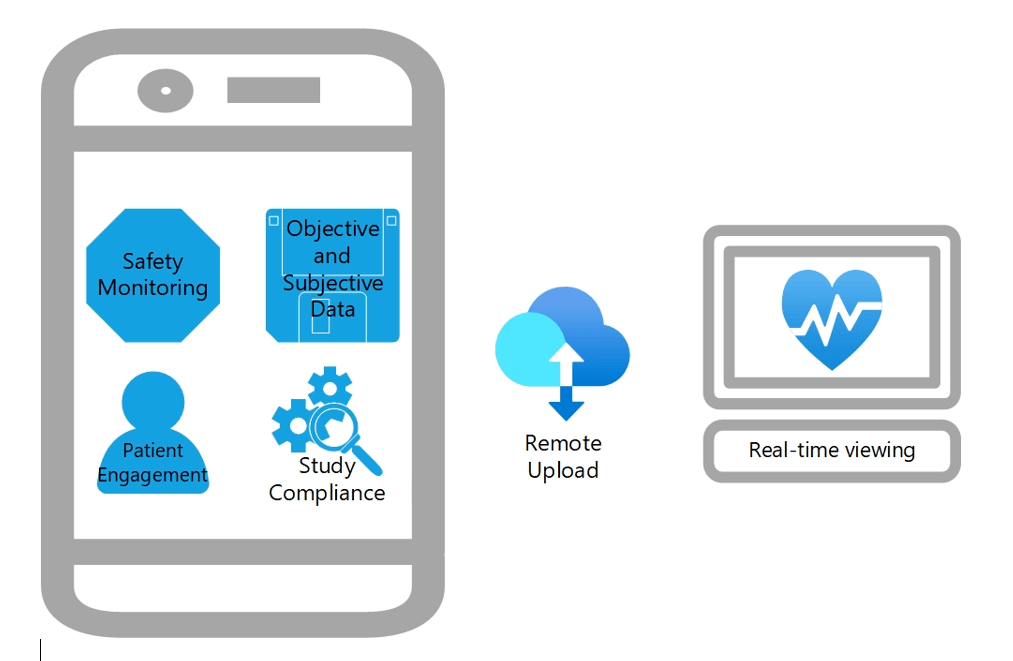
To increase the voice of the patient during clinical trials, integrating patient-reported outcomes (PROs) with clinical outcome assessments and performance outcomes is strongly recommended. In early 2022, FDA released a guidance about how to incorporate PROs in medical device evaluations. PROs and outputs from digital health technologies (DHTs) such as wearable devices can predict adverse events and clinical outcomes. These wearables can continuously monitor patients’ vital signs including heart rate, sleep patterns, physical activity, and other markers of health in real-time. On-demand and scheduled questions can also be easily answered on a wearable device that can promote patient engagement and compliance with the study (e.g., medication confirmations, activity alerts, appointment reminders).
Many digital health technologies consist of hardware and software components. The hardware is the device itself which usually includes a sensor. The software includes the programs that process the collected data such as a mobile application. Digital health technology can be used to collect a variety of data for endpoints or other outcome measures.
Below is a summary of the advantages and disadvantages of using digital health technologies in clinical studies.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Continuous, real-time monitoring and automatic alerts support patient safety | Continuous, real-time data collection and notifications may seem intrusive |
Collect objective and subjective patient-reported outcomes remotely | Analysis depends on compliance with use of wearable guidelines |
May reduce number of on-site follow-ups | Cost to replace if damaged or stolen |
Engages patients to help improve retention and study compliance |
Regulatory Requirements and Guidances
As the technology of wearable devices continues to develop, regulatory provisions specific to digital health technologies continue to develop as well. For European Union and European Economic Area countries, data privacy and security regulations such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) apply to data from digital health technologies.
FDA has issued a guidance about the use of digital health technologies in clinical investigations. This guidance outlines the considerations for wearable device selection, verification, validation, usability testing, endpoint justification, statistical analysis, and risk assessment. These considerations should be included in the submission of a clinical investigation that proposes the use of a DHT.
Suitability and Selection of a DHT
The goal of selecting a suitable DHT is that it is “fit-for-purpose”. The purpose of the DHT may be to evaluate a study endpoint, to provide safety monitoring, or to encourage a particular level of physical activity. After determining the purpose of digital health technology use in a clinical investigation, consider if it will be suitable for the study population. Age, language, education, technical skills, and geographical location should be included in the selection of a DHT. Population-specific needs can be met through accommodations such as larger text/screens/buttons, translated interfaces, or a simplified menu.
The DHT should also meet the technical and performance specifications needed to achieve its goal in the clinical trial. An example of technical specifications is an offline mode and high storage capacity if collecting continuous data from a rural population. Performance specifications include accuracy, precision, and reliability of the DHT data. These performance specifications may be affected by environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, further highlighting the importance of fit-for-purpose based on the geographical location of the patient population. A sponsor may also consider allowing participants to use their own DHT or other device. This option should also be assessed for fit-for-purpose appropriateness. Note that patients should not be excluded from a clinical investigation if they cannot bring their own device.
Along with the technical and performance specifications, a DHT needs to have a design and operation to be fit-for-purpose for a clinical investigation. If the patient is asked to wear the DHT continuously, then compliance could be affected by comfort. Thus, the material, size, weight, appearance, and portability of the DHT design should be considered. Many DHTs offer real-time feedback to the patient user, which is beneficial to encourage particular behavior, such as walking after a procedure. However, in a blinded or masked study, this feedback may bias behavior in a way that might affect the evaluation of the investigational product. Another important operational feature of DHTs is alerts. Alerts to the user and trial personnel for low battery and incomplete data transmission are valuable to data integrity since corrections can be made in real-time by the user with the assistance of the trial personnel.
Fit-for-purpose also applies to the trial personnel and sponsor, not just the user. The sponsor will need the network systems and personnel capacity to handle the volume of data. The network systems also need to ensure privacy and security of patient data. An application programming interface (API) may be helpful in automatically integrating and processing DHT data.
Verification, Validation, and Usability Evaluations
Evaluations for verification, validation, and usability of the device are considered a part of the fit-for-purpose selection process of a DHT. DHT manufacturers often provide this information in labeling or make reference to testing reports. Check that the evaluation of DHT manufacturer includes the study’s intended patient population. For example, step measurements may be verified for healthy individuals, but not for patients with mobility disorders such as Parkinson’s disease. In addition, data storage and retention procedures should be documented since source data collected from DHT and processed metadata may be requested by the FDA for inspection.
Risks of Digital Health Technologies
As with other methods of data collection, DHTs have risks to patient health, privacy, and rights. The clinical risks include injury from the physical features of the DHT (i.e., skin irritation) and errors in measurement if used to determine treatment. A data security breach can be a privacy and health risk as it may disclose personally identifiable information or corrupt the operation of the DHT. The risks of DHT use should be described in the informed consent and discussed with the patient.
Training
The sponsor should ensure training occurs for trial personnel and trial participants. This documented training includes the plan for technical assistance, risk management, and safety monitoring. The Investigator’s role is to ensure the participants’ and caregivers’ understanding of the DHT use and risks through the informed consent process and training. Note that re-training may be necessary if there are updates or changes to the technology or if data errors or loss need to be corrected.
Conclusion
Digital health technologies offer a way to collect patient reported outcome data via remote data acquisition. Selection of a DHT should be suitable for the study or “fit-for-purpose” as evaluated for verification, validation, and usability. Consideration should be given to the risks and training requirements of DHTs before implementing in a study.
 MED offers a variety of clinical trial services and is a full-service CRO. We have over 40 years of experience designing and executing clinical trials, ranging from early feasibility studies to multinational, controlled pivotal trials to post-market registries.
MED offers a variety of clinical trial services and is a full-service CRO. We have over 40 years of experience designing and executing clinical trials, ranging from early feasibility studies to multinational, controlled pivotal trials to post-market registries.
Contact us today to discuss how you can integrate wearable devices and patient-reported outcomes in your clinical study!
Get email about news, services, and events from MED Institute.
OUR COMMITMENT
We are committed to consistently performing services with high quality, that deliver exceptional results, and add value to the client’s business.
For client surveys sent since 2024, we received ratings of 4.99/5 (16).

